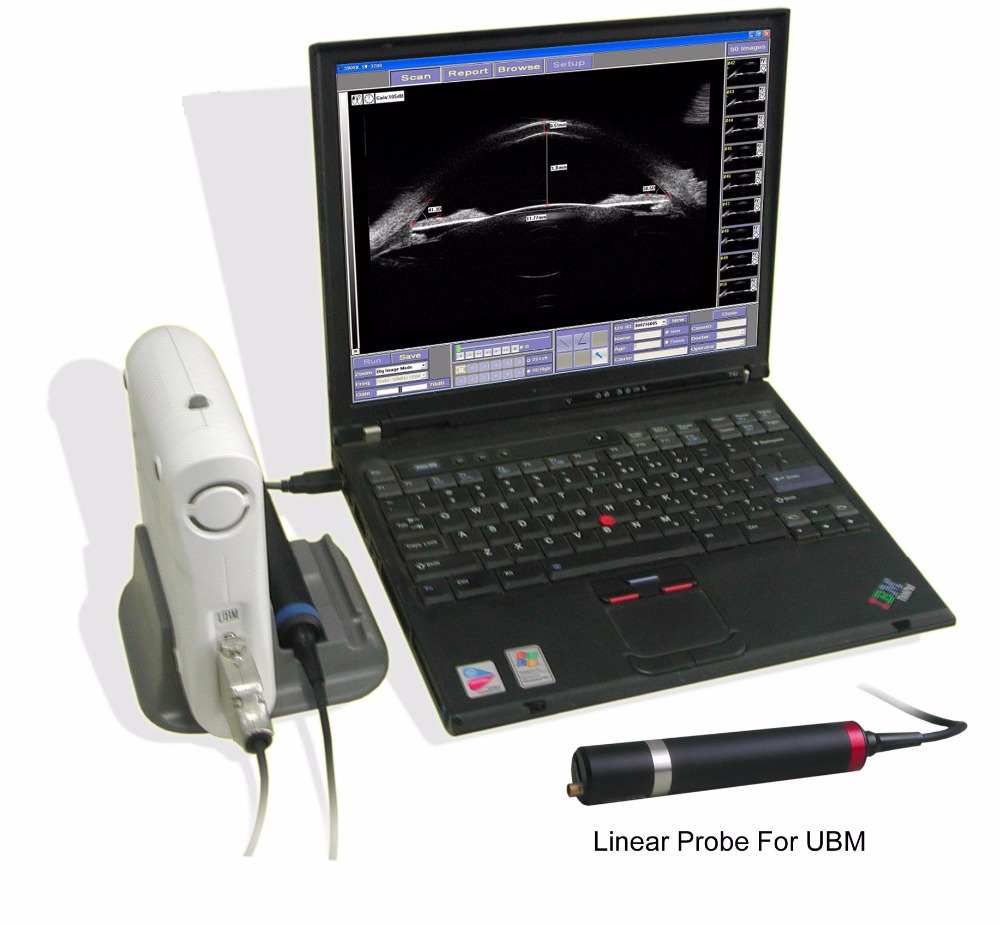
The characteristics of an ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) system like the one shown include several key aspects, including technology, applications, and benefits.
Technology and Specifications:
High Frequency: Uses very high-frequency ultrasound (e.g., 50 MHz) for high-resolution imaging of the anterior segment of the eye.
Resolution and Penetration: Provides very high-resolution cross-sectional images with good tissue penetration, allowing visualization of fine structures such as the cornea, iris, ciliary body, and iridocorneal angle.
Portability: Often designed to be portable, connecting to laptops or desktops via USB, facilitating its use in various clinical environments.
Integrated Software: Works with dedicated software for image acquisition, analysis, and management, often with measurement and reporting features.
Specialty Probes: Uses sheathless oscillating probes designed for ocular examination, sometimes with guards and alarms for patient safety.
Clinical Applications:
Anterior Segment Analysis: Allows for detailed examination of the cornea, lens, ciliary body, iris, and iridocorneal angle.
Glaucoma Diagnosis: Essential for analyzing iridocorneal angle opening and detecting angles at risk of closure.
Evaluation of Ocular Pathologies: Used in the diagnosis and follow-up of various conditions, including ocular trauma, ciliary body disease, and other anterior segment pathologies.
Postoperative Follow-up: Allows for screening for complications after filtration surgery and assessment of reasons for surgical failure.
Benefits:
Detailed Imaging: Provides clear visualization of ocular structures difficult to observe with other methods. Non-invasive: UBM is a non-invasive procedure for analyzing the anterior segment of the eye.
Versatility: Applicable in a wide range of clinical situations for diagnosis, monitoring, and research in ophthalmology.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.