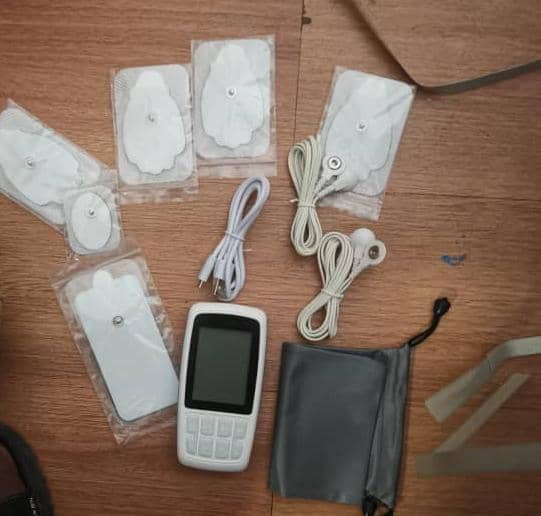
The features of a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) device, such as the one pictured, typically include the following:
How it works: A TENS device is a small, battery-powered unit that delivers a weak electrical current through adhesive electrodes placed on the skin. These electrical impulses stimulate the nerves in the targeted area to help block or alter the transmission of pain signals to the brain.
Components: It consists of a main unit (often the size of a small cell phone), connecting wires, and several sets of adhesive electrodes.
Adjustable settings: The user can typically adjust the intensity, frequency, and duration of the electrical impulses to find a comfortable and effective level.
Operating Modes: TENS machines often offer different modes, such as a continuous mode (constant tingling sensation) and a burst mode (pulsing sensation).
Portability: These devices are generally lightweight and portable, allowing them to be used during a variety of activities, with the exception of showering, swimming, or driving in some cases.
Applications: TENS devices are used to relieve various types of pain, including back pain, joint pain, neuralgia, menstrual cramps, and pain related to musculoskeletal injuries.
Technical Specifications (vary by model):
Frequency: For example, 1 to 250 Hz.
Pulse Width: For example, 20 to 250 microseconds.
Number of Channels: Some models have two or four channels.
Power Source: Often a 9-volt battery or dual power supply (mains/battery).
Display: A graphic LCD display is common.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.