Lead Apron
Personal protective equipment designed to shield medical personnel and patients from ionizing radiation (X-rays) during medical examinations or procedures.
Main Characteristics:
- Protective Material: Made with lead or lead-free composite materials to block X-rays
- Protective Thickness: Lead equivalent typically ranges from 0.25 mm to 0.50 mm, with options for differentiated protection (e.g., 0.50 mm front, 0.25 mm back)
- Design and Styles:
- Available in one-piece styles (e.g., closed apron) or half-sleeve styles
- Includes padded shoulder pads for weight distribution and comfort
- Features waistbands for enhanced lumbar support
- Sizes and Fit: Offered in various sizes (XS to XXL) with custom-made options for optimal coverage
- Weight: Varies by size and lead thickness (e.g., a medium-sized apron with 0.35 mmPb filtration weighs approximately 3.8 kg)
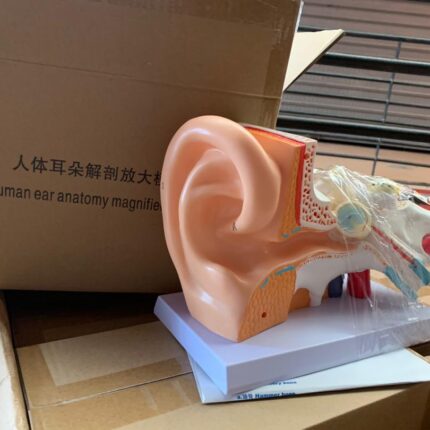
Human Ear Anatomical Model
A detailed, magnified model of the human ear designed for educational purposes in medical and academic settings.
Main Features:
- 5x Magnification: Enlarged five times the size of a real human ear for clear visualization of internal and external structures
- Detachable Design: Disassembles into at least two main parts (middle and inner ear) to facilitate study of overlapping elements
- Sturdy Material: Constructed from durable, wear-resistant PVC plastic with an ABS base for enhanced stability during display or teaching
- Labeled Structures: Precisely labeled parts, including outer ear, middle ear, inner ear, and cochlea, with color-coded sections for easy identification
- Versatile Use: Ideal for educational settings such as schools, hospitals, and laboratories, suitable for students, healthcare professionals, and educators
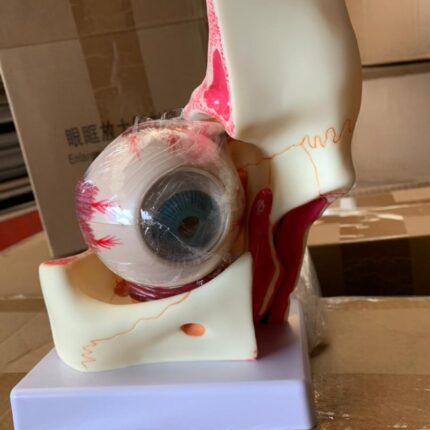
Eye and Orbit Anatomy
A magnified anatomical model of the human eye and orbit, designed for educational purposes in medical and academic settings.
Main Features:
- Magnification: Typically 3x the size of a real human eye and orbit, enhancing visibility of internal and external structures
- Composition and Detachability: Comprises multiple detachable parts (e.g., 10 parts), including the orbit, sclera, cornea, iris, ciliary body, choroid, and retina, allowing detailed study of the eye’s hierarchical structure
- Material: Made from high-quality, durable, and environmentally friendly PVC
- Fidelity and Detail: Features clear textures, high fidelity, and precise details to support accurate understanding of eye anatomy
- Educational Use: Ideal for teaching and studying eye anatomy, suitable for students and medical professionals
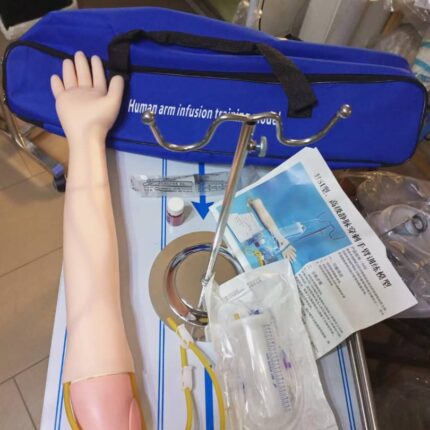
Injection Arm
The IV arm training model, like the one depicted, typically includes these features:
Realistic Design:
Mimics a human arm with adjustable skin and veins, offering a lifelike experience for practicing injections, blood draws, and infusions.
Authentic Puncture Feedback:
Replicates the sensation of needle insertion, including a distinct “pop” and simulated blood return upon correct vein puncture.
Durable and Reusable:
Constructed from high-quality materials, it endures hundreds of punctures without leaking, with self-sealing skin for repeated use.
Included Accessories:
Comes equipped with essential components for comprehensive training, such as an arm stand, fluid containers, and artificial blood.
Versatile Training:
Supports practice of multiple techniques, including IV injections, catheter placement, and blood collection.
Male Reproductive System Anatomical Model
The male reproductive system anatomical model offers a midsagittal view of the male pelvis, showcasing the structure and arrangement of the reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum.
Key Features:
Detailed Visualization:
The midsagittal section provides a clear, in-depth perspective of the male pelvis’s internal anatomy, including reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum.
Structures Highlighted:
Depicts key components such as the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, and urethra, among others.
Material Quality:
Constructed from durable PVC, ensuring accurate representation of anatomical details.
Educational Purpose:
Serves as a valuable medical education tool, enhancing understanding of the male reproductive system’s anatomy and physiology.
Anatomical Model of the Spine
The human spine anatomical model, commonly referred to as the spine, represents the central support structure of the human skeleton, extending from the skull’s base to the pelvis.
Structure and Composition:
Comprised of 33 vertically stacked vertebrae, separated by intervertebral discs that function as shock absorbers.
Segments:
Divided into five regions: 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, 5 lumbar vertebrae, the sacrum (5 fused vertebrae), and the coccyx (3-4 fused vertebrae).
Functions:
Serves three primary roles:
– **Static**: Maintains upright posture.
– **Dynamic**: Enables trunk and head mobility.
– **Protective**: Shields the spinal cord within the spinal canal.
Role:
Supports body weight, facilitates a wide range of movements, and acts as an anchor for muscles and ligaments.
Kidney Anatomical Model
The Axis Scientific Human Kidney Anatomical Model features the following features:
Magnification:
It is magnified to 3 times life size, providing a detailed view of the kidney’s internal anatomy.
Detailed Anatomical Structures:
It displays the renal cortex, renal medulla (with renal pyramids), major and minor calyces, renal columns, renal pelvis, ureter, renal artery, and renal vein.
Adrenal Gland Included:
The model also includes the adrenal gland, located above the kidney.
Materials: It is generally made of high-quality, environmentally friendly, and durable PVC.
Structure Numbering:
The various anatomical parts are numbered and accompanied by a detailed manual to facilitate identification and learning.
Support Base:
The model is mounted on a stable, white base and can sometimes be removed for further study.
Educational Use:
It is designed as an ideal educational and teaching tool for anatomy and physiology students, as well as for healthcare professionals for patient education.
Dental Anatomy Model
Features of the Dental Demonstration Model:
Materials:
Constructed from non-toxic, eco-friendly polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic.
Structure:
Features a full set of 32 fixed teeth, soft gums, and an included tongue for realistic representation.
Function:
Designed to demonstrate proper dental hygiene, especially correct toothbrushing techniques.
Use:
Serves as an effective educational tool for dental students, dentists (for patient instruction), and teachers (to promote good oral habits in school and kindergarten settings).
Simulation:
Boasts naturally colored gums and highly durable teeth with accurate anatomical shaping.
Durability & Maintenance:
Resistant to corrosion and easy to clean and disinfect for long-term use.
CPR Manikin
**Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) Manikins**
CPR manikins are lifelike training tools designed to replicate human anatomy, enabling users to practice life-saving first aid techniques.
**Key Features:**
✔ **Realistic Anatomical Landmarks** – Includes clearly defined sternum and ribs for accurate hand placement during chest compressions.
✔ **Thoracic Simulation** – The rib cage offers human-like resistance to mimic real cardiac massage conditions.
✔ **Multiple Size Options** – Available in adult, child, and infant models to train for various emergency scenarios.
✔ **Quick Response (QCPR) Technology** – Advanced feedback system to monitor and improve CPR performance in real time.
Anatomy of the Human Urinary System
### **Human Urinary System – Key Features**
The urinary system consists of specialized organs that work together to filter blood, remove waste, and maintain fluid and electrolyte balance.
**Kidneys**
– Paired, bean-shaped organs that filter blood to eliminate waste (e.g., urea, excess salts).
– Regulate blood pressure, electrolyte levels, and red blood cell production.
**Ureters**
– Two narrow tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
**Bladder**
– A muscular, expandable sac that stores urine (capacity: ~600 mL).
– Contracts during urination to expel urine.
**Arteries & Veins**
– Represented in red (arteries) and blue (veins) on models.
– Supply blood to the kidneys for filtration and oxygenate urinary tissues.
**Urethra**
– The final passageway for urine excretion from the bladder to the exterior.
Anatomical Model of the Human Pelvis Skeleton
Anatomical Model of the Female Pelvis – Key Features
This detailed anatomical model accurately represents the structure and function of the female human pelvis, designed for both educational and clinical applications.
Bone Composition:
-
Includes paired iliac (coxal) bones, sacrum, and coccyx
-
Features L1 and L2 lumbar vertebrae to demonstrate spinal articulation
-
Provides complete representation of pelvic skeletal anatomy
Structural Characteristics:
-
Distinctive funnel-shaped architecture divided into:
-
Greater pelvis (false pelvis): Upper, flared portion
-
Lesser pelvis (true pelvis): Lower, narrower cavity
-
-
Anatomically accurate female morphology:
-
Wider, more circular pelvic inlet
-
Broader subpubic angle
-
Shorter, more everted sacrum
-
-
Designed to reflect obstetric adaptations for childbirth
Functional Attributes:
-
Supports weight transfer between trunk and lower limbs
-
Provides attachment points for major muscle groups
-
Protects reproductive organs and lower abdominal viscera
-
Facilitates bipedal locomotion and spinal stability
Educational & Clinical Applications:
-
Essential teaching tool for:
-
Medical and nursing education
-
Physical therapy programs
-
Midwifery training
-
-
Valuable clinical reference for:
-
Obstetric and gynecological practice
-
Orthopedic assessments
-
Surgical planning
-
-
Enables detailed study of:
-
Pelvic dimensions and variations
-
Biomechanical relationships
-
Pathological conditions
-
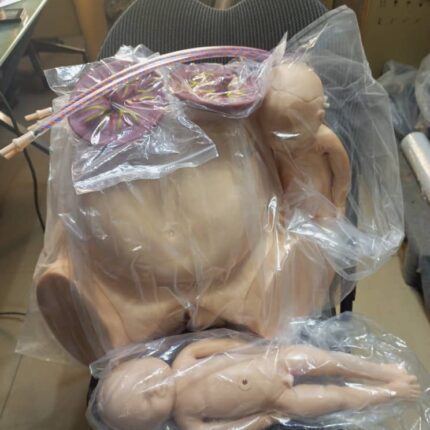
Birthing Pelvis with 2 Babies (Male and Female)
The birthing pelvis is the female bony structure essential for childbirth, providing both structural support and a dynamic passageway for fetal delivery.
Anatomical Composition
-
Comprises four fused bones:
-
Paired iliac bones (forming the pelvic girdle)
-
Sacrum (posterior base of the spine)
-
Coccyx (tailbone)
-
-
Connects the spine to the lower limbs, ensuring stability and weight distribution.
Shape & Structural Divisions
-
Funnel/hourglass shape with distinct regions:
-
Upper flare (false pelvis): Wider, supports abdominal organs.
-
Lower flare (true pelvis): Narrower, forms the birth canal.
-
-
Superior strait: The narrowing between these regions, a critical landmark for obstetric assessment.
Obstetric Straits & Key Measurements
The pelvis features three key straits, each with critical diameters for fetal passage:
-
Upper strait:
-
Promontoretropubic diameter (anteroposterior measurement).
-
-
Middle strait:
-
Median transverse diameter (widest point between ischial spines).
-
-
Lower strait:
-
Interspinous diameter (between ischial tuberosities).
-
-
These measurements determine cephalopelvic disproportion (CPD) and delivery feasibility.
Dynamic Adaptability
-
Not rigid: Hormonal changes (relaxin, progesterone) increase ligament laxity late in pregnancy.
-
Pubis symphysis and sacroiliac joints slightly widen, expanding the birth canal by up to 10–15%.
Role in Childbirth
-
Guides fetal descent: The baby navigates through the pelvic inlet, mid-cavity, and outlet.
-
Facilitates rotation: Bone contours help the fetus rotate into optimal positioning (e.g., occiput anterior).
-
Enables vaginal delivery: Optimal pelvic dimensions and adaptability prevent obstructed labor.